Food Chain Definition Examples Biology Diagrams A food chain is a linear network of links in a food web, often starting with an autotroph (such as grass or algae), One way keystone species impact an ecosystem is through their presence in an ecosystem's food web and, by extension, a food chain within said ecosystem. [21]

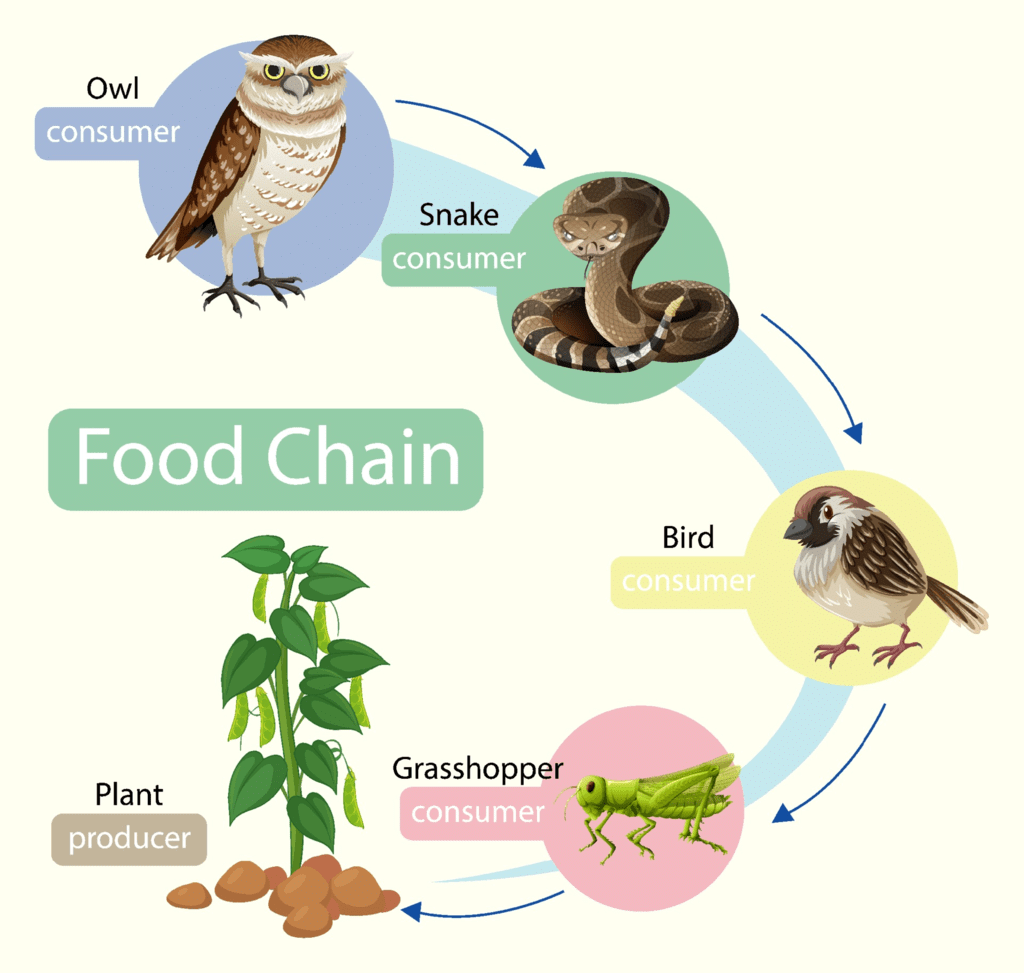
A food chain in a grassland ecosystem may consist of grasses and other plants, grasshoppers, frogs, snakes and hawks (Figure 8.3). In a freshwater aquatic ecosystem like a pond, the organisms in the food chain include algae, small animals, insects and their larvae, small fish, big fish and a fish-eating bird or animal (Figure 8.4).

National Geographic Society Biology Diagrams
These food chains are interconnected, which leads to the formation of complex food webs that tell us about the relationship between multiple organisms and their interactions. Food chains are categorized based on the role of organisms in the ecosystem and are named: Detritus Food Chain, Grazing Food Chain, and Parasitics Food Chain.

A food chain is a fundamental concept in ecology, illustrating how energy and nutrients move through an ecosystem. Food chains reveal the relationships between organisms, showing how each organism plays a role in maintaining ecological balance. By studying food chains, ecologists better understand ecosystem dynamics, including the flow of Learn what a food chain is, how it shows the feeding relationships and energy flow in an ecosystem. Explore the types of food chains, such as detritus and grazing, and their examples with BYJU'S Biology.
Definition, Parts, Types, and Examples Biology Diagrams
Food Chains. A food chain is a linear sequence of organisms through which nutrients and energy pass as one organism eats another; the levels in the food chain are producers, primary consumers, higher-level consumers, and finally decomposers. These levels are used to describe ecosystem structure and dynamics. There is a single path through a
